By Frances Huang
.png)
As a medical worker, we all know that medication safety is always an important issue, major, and most rewarding task in patient safety. In response to 2022 WHO World Patient Safety Day, Joint Commition of Taiwan (JCT) held a series of forums to discuss from polypharmacy, reconciliation, introducing new IT technology into the medication process to improve medication safety. However, there are discussions and new issues keep coming up.In the webinar held on 19th September, Dr. Pa-Chun Wang who is Chairman of ASQua and CEO of Joint Comission of Taiwan, delivered his open remarks with “Medication Safety” to highlight the topic of the webinar today.
Heal | Learn |Discover
Prof. Jefferey Braithwaite, President of ISQua and Founding Director of Australian Institute of Health Innovation, believe that medical workers heal, learn, and discover during the clinical medication process. Australian Institute of Health Innovation (AIHI) encourage joint and cross-field research and studies to explore solutions for the medical field. Prof. Jefferey Braithwaite also introduce the vision and the mission of International Society for Quality in Health Care which is to ne the leader of transformation in health and health care, and to inspire, drive improvement in health, safety, and quality of healthcare worldwide.
Prof. Jefferey Braithwaite shared some of his observations on patient Safety and had provided an interesting point that the amazing thing about the healthcare is it produces safe care in 90% of cases not it produces adverse events in 10% of all cases. We should focus and review how things go right, not focusing on reviewing why things go wrong. There are two types of Safety, Safety -I and Safety-II. The idea of Safety-I is to focus on how to reduce the adverse event and try not to make mistake in medical procedure as possible as they can, however, Safety-II is to increase the acceptable result as much as possible which means try to make sure the medical procedures go right. Safety-I and Safety-II are different from the mindset. Most of the people don’t care how these well cared cases can be done in the right way and what did they do to keep the patient safe. If we can enhance and keep a positive mindset while we taking care of the patient, will we increase the rate of medication safety?
According to the research published by WHO, the expense globally associated with medication errors cost 41 billion USD annually and the research also shows that most of the medication errors are preventable. Though the IT technology seems promising in making significant impact on medication safety, but as Dr. Wang mentioned in the beginning of the webinar today, the technology also creates new types of errors we had never met before. However, IT technology did reduce the rate of human errors and improve the efficiency of medical workers. For most of the medication errors are preventable, WHO set the goal that we should make our best to reduce at least 50% of the avoidable harm related to medications over 5 years globally. Hopefully we can work hand in hand to achieve the goal together.
Closed Loop Management on High-Alert Drug
Dr. Hui-Yu Chen, Pharmacy Department Director in Linkou Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan, shared their experience of applying IT technology in patient safety management. The most important progress and improvement of patient safety in Taiwan is that Ministry of Health and Welfare had entrusted JCT to develop a target of patient safety in 2004 and established general principles for medical workers to follow to enhance the patient safety, such as promoting integrated medical service, enhance the safety of care for patients who need high alert medication, enhance the safety of infusions that require controlled flow rates or shared lines.
Chang Gung Hospital adopting closed loop management as a solution on high alert drug, the workflow is a closed loop as follows,
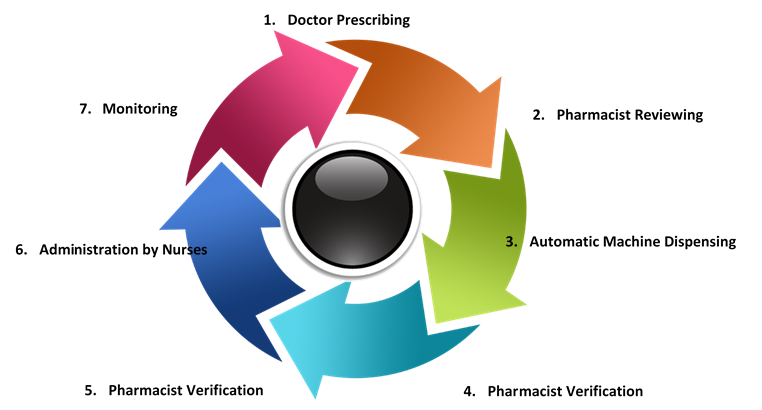
The Closed Loop Management of High Alert Drug can make sure the accuracy and the safety of medication procedure. The medicine is tagged in different color according to the category in the system to remind the doctor about their prescription, the pharmacist checking the prescription with the system, and the pharmacist will check again after the dispensing done by auto dispensing system with Scanning QR Code to review is the medicine matches the prescription. All the medical workflows will be recorded in the system for nurses and doctors as reference for medical decision or follow-up healthcare.
Through the closed loop management, auto dispensing system and the integrated medical information, medical workers can save their time and contribute more on their professional skills suck as pharmacy, treating patient, providing healthcare with better quality. What’s more, the smart recording system help reduce common human errors in dispensing or misreading of handwriting. With the integrated medical system applied, the data can be collected and recorded automatically, improve the accuracy and efficiency of medical workflow.
Medication Safety: Transition of Care
According to the research of medical adverse event in Japan, amount all the medication error in near-miss event, 35.4% related to medication. In adverse event, 8.1% caused by medication error. Especially when patient journey across different transitions of care and medication processes, to ensure the medication safety is important for the patient safety. Prof. Shin Ushiro, Divisional Director of Patient Safety Division of Kyushu University Hospital in Japan, shared the workflow in Kyushu University Hospital that how Pharmacist play a key role to ensure patient safety during the transitional care process.
In Kyushu University Hospital, pharmacist will audit the medication carried-in drug, interview with the patient to know is the patient has any side-effect or allergy to the medication. Pharmacists will enquire, collect and recorded patient’s effect to the medication and propose alternative prescription to the physician such as appropriate amount, route, or formulation. At the meanwhile, pharmacist also play an important role in communication between physician and nurse on patient’s medication, therapy and clarify the questionable prescription. Pharmacist providing education to the patient on admission on medication therapy, participate clinical conference and related research.
In Japan, there’s a job manual for ward pharmacist and specific procedures and workflow for them to follow. Pharmacists need to record the interview with patient on admission, verify and register the carried-in drugs, patient education on medication therapy on Electronic Health Record (HER). Pharmacist using digital verification application “TEBUN NAVI” to verify the medication by scanning PTP which has GS1 barcode on the package to accelerate the work efficiency and process, pharmacist also help other nurses on verify the medication therapy.
Medication safety is a highly alerted issue in Japan, even there’s a comic book Unsung Cinderella MIDORI, well describe a patient ward pharmacist’s workflow in detail which has improved people’s knowledge about how pharmacist play an important role in the medication process and how they do to keep patient safety. Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare using the character in the comic as a key image of the Week of Medication and Health. To improving patient safety and medication safety, JQs review all the adverse event related to medication error and prescription error regularly, emphasizing the high risk of prescription error in carried-in drugs and raising medical workers’ attention on the importance of audit the carried-in drugs, interview with the patient for preventing the medication error. Patient safety is the basic required knowledge for medical student in Japan, student must learn and know how to interact and build the care relationship with patient, how to explain the prescription and medication therapy to the patient.
Medication Safety: Polypharmacy
Dr. Sanjeev Singh, Medical Director at Amrita Institute of Medical Science in India, address that India should pay more attention to the issue of polypharmacy for the adverse event related to medication errors in India only 0.04% of the total while adverse event related to medication error 3.2% of the globally.
So far, we still lack a universal definition about “polypharmacy.” According to the definition of polypharmacy described by WHO, polypharmacy means “the administration of many drugs at the same time or the administration of excessive number of drugs.” Usually, when there are more than five drugs, we can say that is polypharmacy. Moreover, Dr. Sanjeev Singh emphasized that medical workers should consider the potential risk over the counter, prescription and/or traditional and complementary medicines as part of polypharmacy as well.
Polypharmacy could cause multiple negative consequences, such as increasing the risk for adverse events, drug-drug, and drug-disease interactions, reducing functional capacity. Polypharmacy also leads to multiple geriatric syndromes, medication non-adherence, increased mortality, and increased the cost of health care. Those effects guiding us to stay focus on the potential risk can cause harm to patient. BEERS Criteria is a good tool for us to know the potential risk of medication on the drug-disease interactions before giving a prescription. Through the electronical prescription, integration of patient information and medical history, medical workers can choose a better medication therapy for the patient to prevent the risk of potential negative effect which could cause harm to the patient while patient are taking multiple medication during the transitional of care. Dr. Sanjeev Singh mentioned medical workers should follow the 7 steps to appropriate polypharmacy which suggested by WHO. By reviewing the 7 steps, we can understand the necessity of intensive and well communication between patient and doctor. Does the patient understand and welling to take the medication therapy? Does the patient fully understand about the prescription, the medical therapy, and the potential risk of it? Especially when using high alert medication, we should audit and use existing medical information tool such as BEERS Criteria, STOP, Medi-Cog to review the prescription before making medical decision. By doing so, we can reduce and well control the risk of harm to patient caused by polypharmacy.
On the day of World Patient Safety, ASQua appeal for medical family that we should stay focus on the patient safety during the medical process, to reach the goal that WHO set which is to reduce 50% of the adverse event caused by medical errors within 5 years. Not only provide patient with care, but also provide medical care on a patient safety-first basis.
The JCT established the Health Smart Taiwan (HST) , a one-stop portal designed to promote Taiwan's high-quality smart healthcare solutions since 2019. HST combines Taiwan's cutting-edge smart healthcare solutions with the demo site in Taiwan, helping visitors to fully understand the application and development potential of smart healthcare, while creating a new model for smart hospitals. In addition, JCT also welcomes healthcare partners from all over the world to come to Taiwan for face-to-face exchanges on the application of innovative medical technologies.