Applying AR and VR to Greatly Improve Clinical Skills of New Physicians
HST Coverage
Endotracheal intubation and central line insertion are two important core skills in acute and critical care; they are invasive and highly risky. Despite thorough simulation and training, in cases of required refreshing courses in the future to address difficulties, not only there is limited lime for instructions, participants seldom have the opportunity to review what are learned spontaneously in order for them to be well trained and skilled. Meanwhile, while the instructor is demonstrating key detailed-oriented steps inside the oropharynx and the narrow portion of the neck, with participants squeezing together next to the instructor and watching closely, it interferes with the instructor's demonstration and makes it impossible for the participants to watch clearly, either. Upon completion of the training, as a result, they leave still with the lack of confidence and feeling highly anxious. During hands-on, with the instructor evaluating at a close distance, participants' performance can also be affected and it increases the risk of needle stick and related infections.
Taipei Veterans General Hospital applies AR&VR and has designed a self-learning mechanism to help with simulation and training. Ideas throughout the care process are combined together, including hand hygiene, putting on and off protective clothing, endo-tracheal intubation, and central line insertion placement, among others. The emphasis over continuous and total care by the critical care unit is reinforced. This simulation and training tool enables newly hired healthcare professionals to seek self advancement. By wearing the AR glasses and the head-mounted VR system, practice may be repeated and reinforced, even in the case of the difficult intubation class so that participants can learn integrally, time-efficiently, automatically, and dynamically. It helps improve the learning efficiency and also the care capability of the team as well as the patient's family's satisfaction with the safety and service.
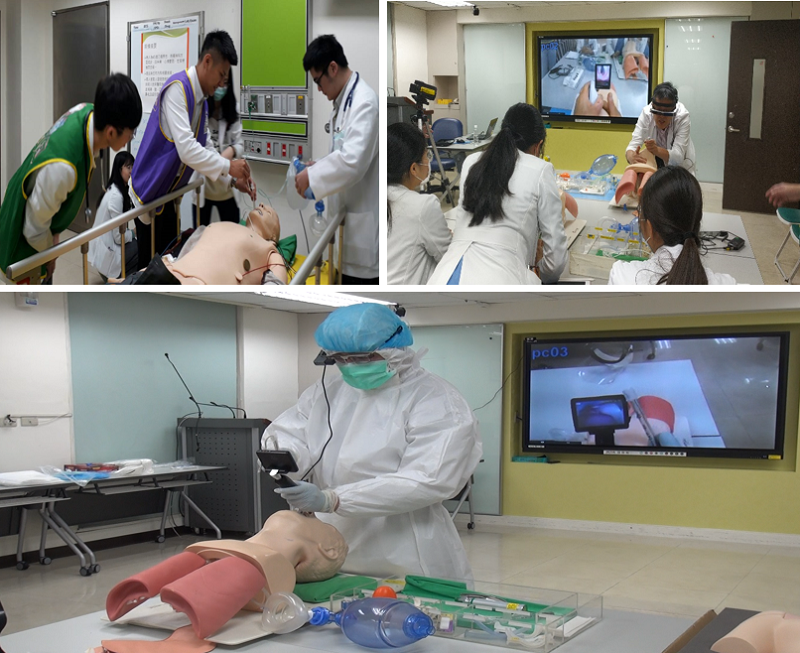

(Figure 1) AR-simulated endotracheal intubation
Training in the past included pre-service training, simulated training, or certifying tests. Nevertheless, students were somewhat frightened while in the clinical setting. As a result, the rate of successful first attempts was never high. By combining the AR&VR simulation and training in addition to smart information technology aids and media, Taipei Veterans General Hospital has managed to reduce the manpower and resources required for arranging refreshing courses. With this advanced self-learning model, the rate of successful first attempts has been greatly enhanced.
Timely Feedback in Clinical Application for Improved Learning Outcome for Participants
Director Ling-Yu Yang at the Education Department of Taipei Veterans General Hospital indicates that among respiratory therapists, nurses, young physicians, including interns, PGY doctors, and first-year residents at the critical care unit, about 10 are receiving the training each month on average and it has been ongoing for three to five years so far, with about 4 to 500 participants accumulatively.
With the AR technology, demonstration films are built in the AR glasses and detailed instructional steps can be projected onto a large screen for all participants to view clearly. The bilateral interaction through AR glasses helps precisely evaluate the accuracy of participants' hands-on performance while at the same time enabling multiple participants to view what is demonstrated by the instructor clearly. While the participants are operating, teachers can also observe conveniently and provide feedback and take pictures through voice control so that students get to see how they do. For areas that participants do not understand, pictures can also be taken applying the AR glasses voice-control technology and uploaded as the timely feedback provided by the instructor.
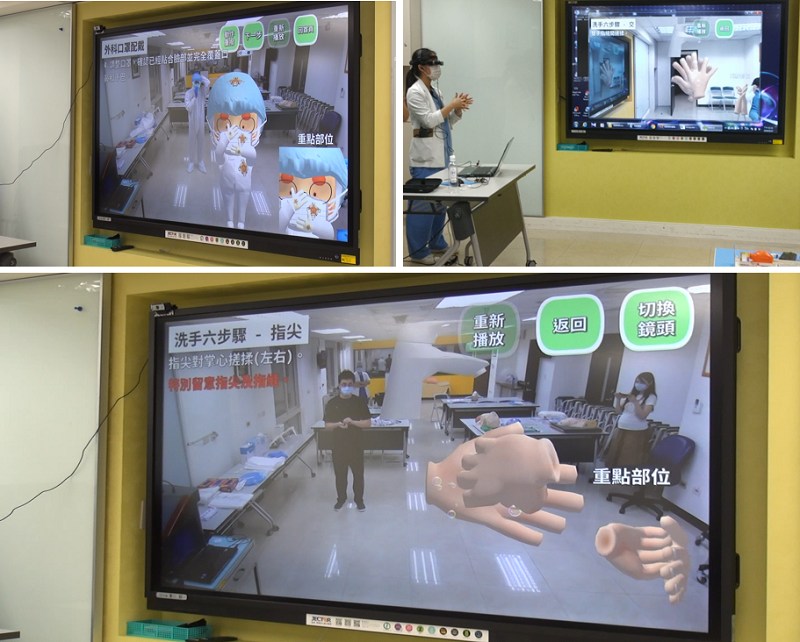

(Figure 2) AR-guided hand wash and wearing of personal protective equipment (PPE)
As far as the thoroughness in technical performance is concerned, improvement has been noted with the introduction of AR&VR simulation and training. Director Ying-Ying Chen at the Division of Clinical Technical Training of Taipei Veterans General Hospital indicates that endotracheal intubation consists of approximately 15 steps and central line insertion placement about 10. In terms of thorough performance following the training, the group where AI glasses were used showed a higher ratio in completely carrying out related steps after the training. As for hand wash and putting on/off the personal protective equipment, the error rate dropped. For the practice in needlestick or sorting out waste with the assistance of VR, the abnormality incidence for the first three months following introduction of the system dropped, too.
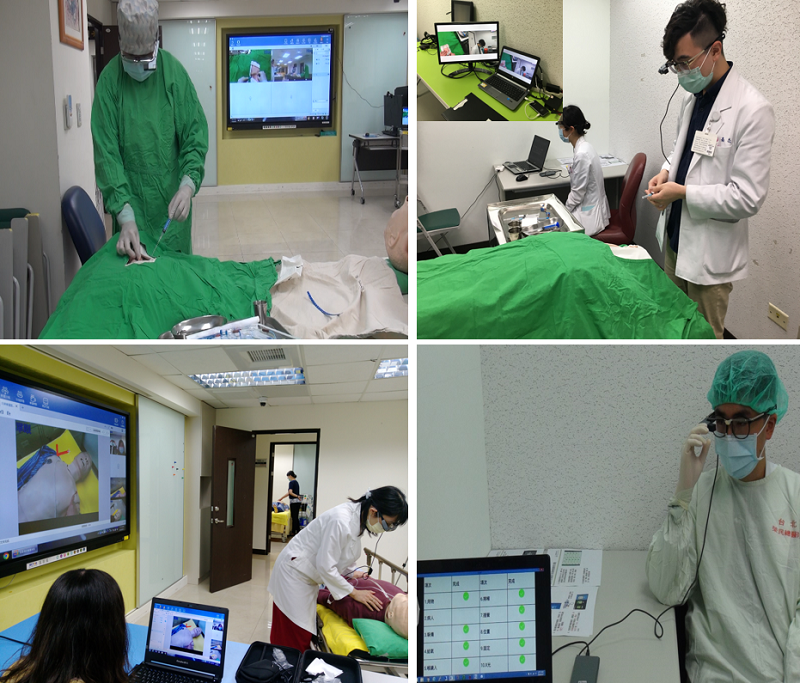
(Figure 3) AR-simulated central line placement
Extended Application in Shared Decision Making to Facilitate Communications Holistic Care Model
Strengths of VR include training in a safe setting for reduced infections, that users will feel real while performing the task, that it is highly convenient from the pedagogical point of view, precise communication of teaching information, that learning can take place at any time anywhere. Newly hired healthcare professionals can choose a suitable informative tool according to the properties of the patient's family in order to provide the family with information precisely.
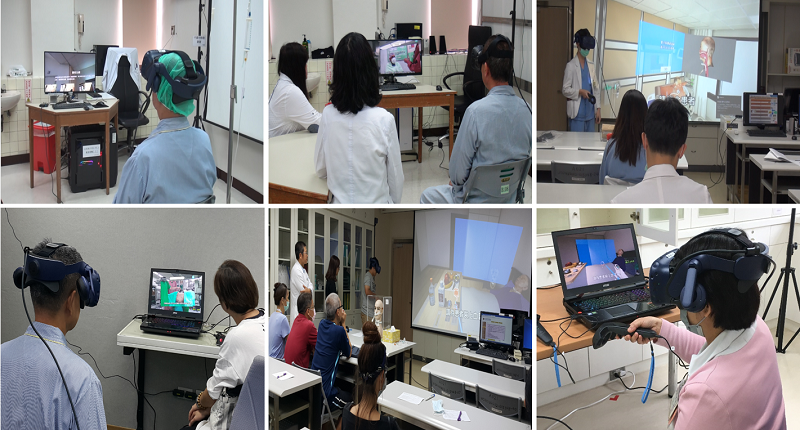

(Figure 4) Family and participant trying out the VR screen
Director Ling-Yu mentions that while developing the doctor-patient shared decision-making aid, the R&D team at the Taipei Veterans General Hospital carefully designed it with the hospital in the background so that participants can use it in environment they are familiar with. From demand assessment, procedural steps, to expected output and even its promotion, the whole training module shows the detail-oriented essence of the team. What makes use even more proud is that it covers total care and everything from the acute phase to the chronic phase and is completely patient-centered. In a training on care ideas, this is an optimal design.
Among the patients in the intensive care unit, the number of timely tracheotomy SDM cases has increased. The complications as a result of improper care following tracheotomy have dropped and the ex-tubing rate has increased. The skills of healthcare professionals in applying this while actually caring for patients have improved. Accomplishments are noted in both patient communication and education. The training provided has cover the individual, familial, procedural, and teamwork levels.
Best Gratitude for Supervisory Support and Team Insistence Along Research and Development
The development process included finding suitable topics, preparing the lesson plan, creating forms and tables, selecting the actual clinical materials, recording the demonstrative films, and simulating the scenarios as well as constant modification. Each lesson plan involved more than 50 meetings. Next to be introduced will be VR simulation and training of ablation in case of arrhythmia.
Director Ling-Yu Yang at the Education Department of Taipei Veterans General Hospital indicates that AR&VR emphasizes hands-on and knowledge-based training. As such, existing teaching materials are needed to fulfill the formation of communication and interactive skills. The AR&VR-combined simulation and training outcome is for the benefit of not only the learners but also for quality care of patients. This package covers the intubation training in the ICU, assistance provided to patient while the latter makes medical decisions, and also long-term post-tracheotomy care following hospital discharge where total care is needed. The required skills, knowledge, and attitudes may somewhat be different. Hand wash, putting on the isolation gown, and intubation are technical while assistance provided in doctor-patient communication is more about knowledge and attitude. With more mature AI technologies in the future, it can also be anticipated to simulate patient communication as part of doctor-patient interaction that will be further combined.
The application of AR&VR has helped the Taipei Veterans General Hospital in terms of precise learning and paper-less environmental protection. The vivid images instead of boring text make one feel real and are interesting. It helps inspire learners and improve the learning efficacy, minimizes difficulty encountered in arranging courses, makes it possible for one to experience a virtual medical process. It is a highly future-oriented clinical tool in medical education.